In this article, you will learn how to perform the various steps needed to create an iPhone application that uses the APNs.
Generating a Certificate Request
The first step to using the APNs is to generate a certificate request file so that you can use it to request for a development SSL certificate later on.
1. Launch the Keychain Access application in your Mac OS X.
2. Select Keychain Access'Certificate Assistant'Request a Certificate From a Certificate Authority (see Figure 1):
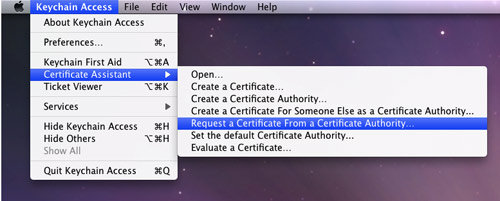 Figure 1
Figure 1. Generating a certificate request
Enter the information required and check the Saved to disk option. Click Continue (see Figure 2).
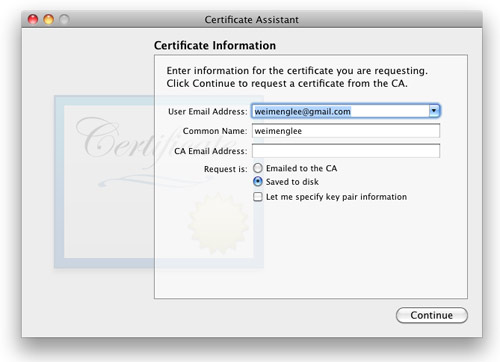 Figure 2
Figure 2. Saving the certificate request to disk
Save the certificate request using the suggested name and click Save (see Figure 3): Click Done in the next screen.
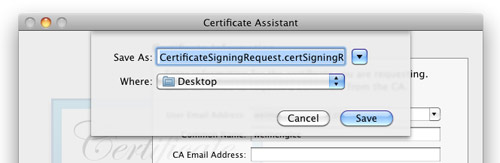 Figure 3
Figure 3. Naming the certificate request
Creating an App ID
Each iPhone applications that uses the APNs must have a unique application ID that uniquely identifies itself. In this step, you will learn how to create an App ID for push notification.
1. Sign in to the iPhone Developer Program at:
http://developer.apple.com/iphone/. Click on the iPhone Developer Program Portal on the right of the page (see Figure 4).
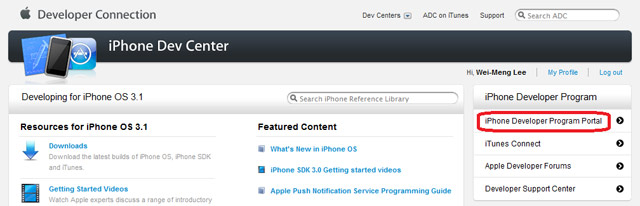 Figure 4
Figure 4. Launching the iPhone Developer Program Portal
You should see the welcome page (see Figure 5).
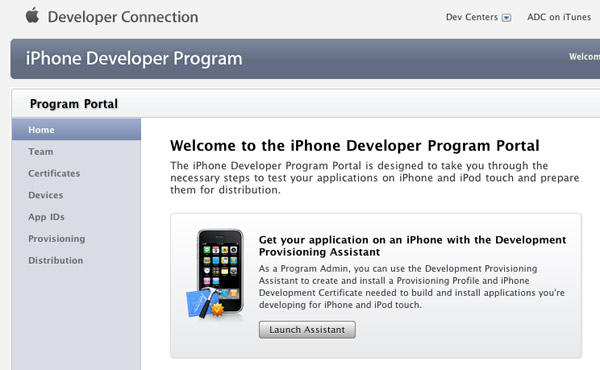 Figure 5
Figure 5. The welcome screen of the iPhone Developer Program Portal
Click on the App IDs tab on the left and then click on the New App ID button (see Figure 6).
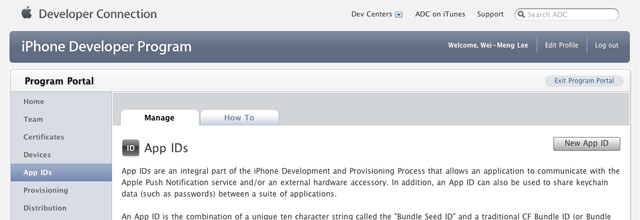 Figure 6
Figure 6. Clicking on the App ID tab
Enter "PushAppID" for the Description and select Generate New for the Bundle Seed ID. For the Bundle Identifier, enter
net.learn2develop.MyPushApp. Click Submit (see Figure 7).
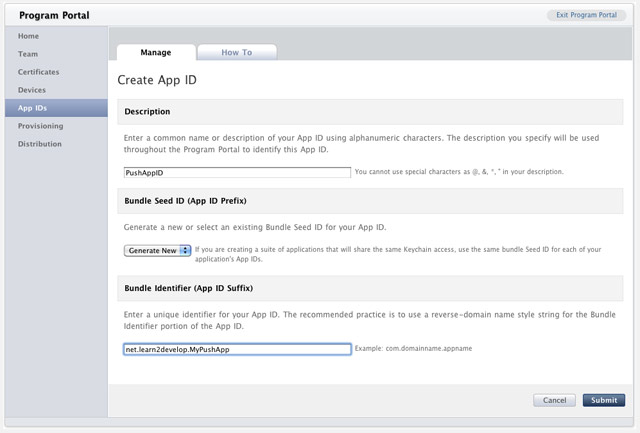 Figure 7
Figure 7. Creating a new App ID
You should now see the App ID that you have created (together with those you have previously created) (see Figure 8).
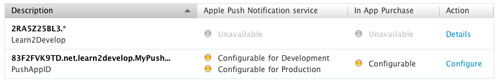 Figure 8
Figure 8. Viewing the newly created App ID
Configuring an App ID for Push Notifications
Once an App ID is created, you need to configure it for push notifications.
1. To configure an App ID for push notification, you need to click the Configure link displayed to the right of the App ID. You will now see the option (see Figure 9).
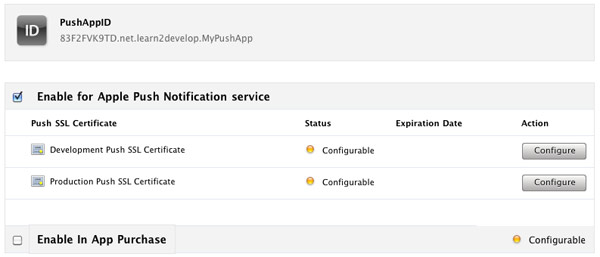 Figure 9
Figure 9. Configuring an App ID for push notification service
Check the Enable for Apple Push Notification service option and click the Configure button displayed to the right of the Development Push SSL Certificate.
2. You will now see the Apple Push Notification service SSL Certificate Assistant screen. Click Continue (see Figure 10).
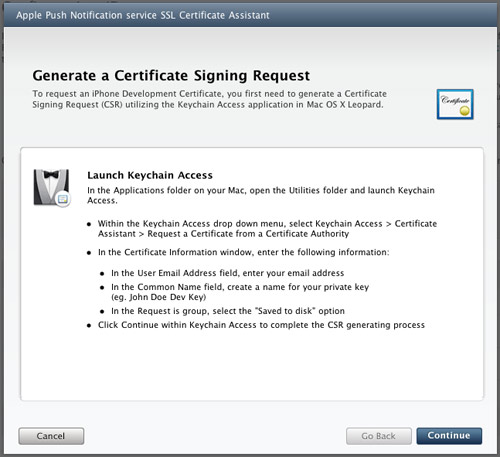 Figure 10
Figure 10. The Apple Push Notification service SSL Certificate Assistant screen
Click the Choose File button to locate the Certificate Request file that you have saved earlier. Click Generate (see Figure 11).
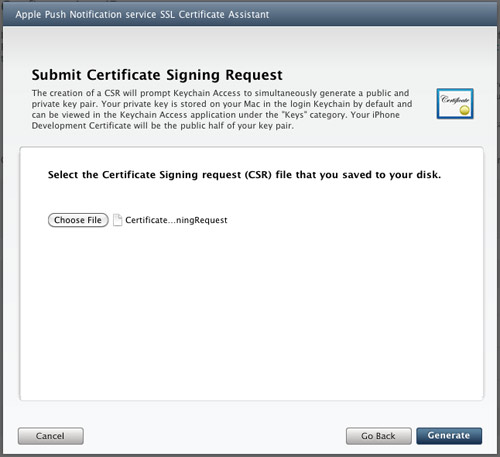 Figure 11
Figure 11. Generating the SSL certificate
Your SSL Certificate will now be generated. Click Continue (see Figure 12).
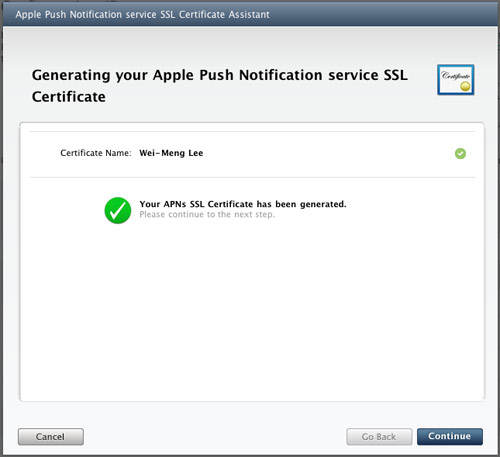 Figure 12
Figure 12. The APNs SSL certificate that is generated
Click the Download Now button to download the SSL Certificate. Click Done (see Figure 13).
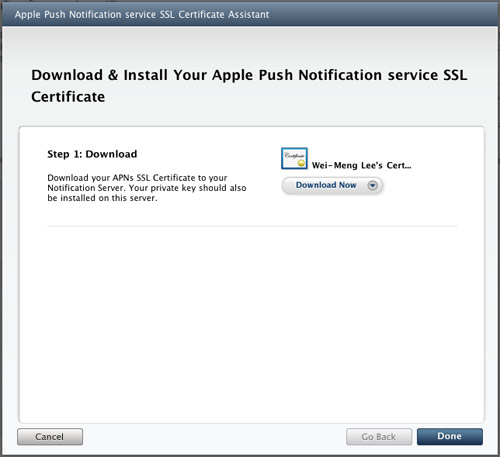 Figure 13
Figure 13. Downloading the certificate generated
The SSL Certificate that you download is named
aps.developer.identity.cer. Double-click on it to install it in the Keychain Access application (see Figure 14). The SSL certificate will be used by your provider application so that it can contact the APNs to send push notifications to your applications.
 Figure 14
Figure 14. Installing the generated certificate into the Keychain Access application
Creating a Provisioning Profile
The next step is to create a provisioning profile so that your application can be installed onto a real device.
1. Back in the iPhone Development Program Portal, click on the Provisioning tab and click on the New Profile button (see Figure 15).
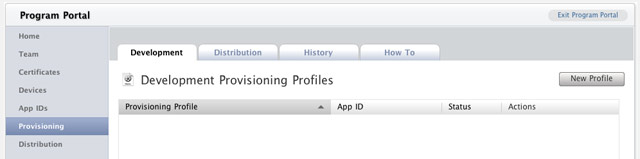 Figure 15
Figure 15. Selecting the Provisioning tab
Type in
MyDevicesProfile as the profile name. Select PushAppID as the App ID. Finally, check all the devices that you want to provision (you can register these devices with the iPhone Developer Program Portal through the Devices tab). Click Submit (see Figure 16).
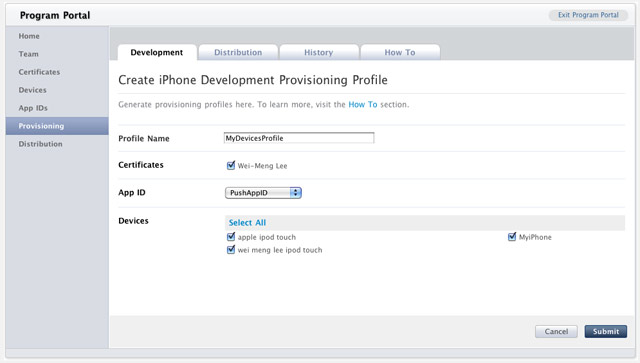 Figure 16
Figure 16. Creating a new provisioning profile
The provisioning profile will now be pending approval. After a while, you will see it appear. Click on the Download button to download the provisioning profile (see Figure 17).
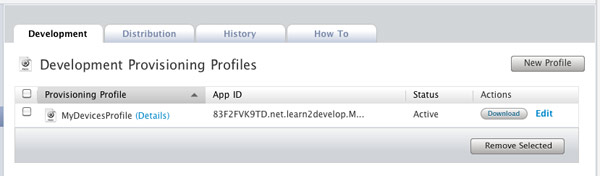 Figure 17
Figure 17. Pending the approval of the provisioning profile
The downloaded provisioning profile is named MyDevicesProfile.mobileprovision.
Provisioning a Device
With the provision profile created, you will now install it onto a real device.
1. Connect your iPhone or iPod Touch to your Mac.
2. Drag and drop the downloaded
MyDevicesProfile.mobileprovision file onto the Xcode icon on the Dock.
3. Launch the Organizer application from within Xcode and select the device currently connected to your Mac. You should see the
MyDevicesProfile installed on the device (see Figure 18).
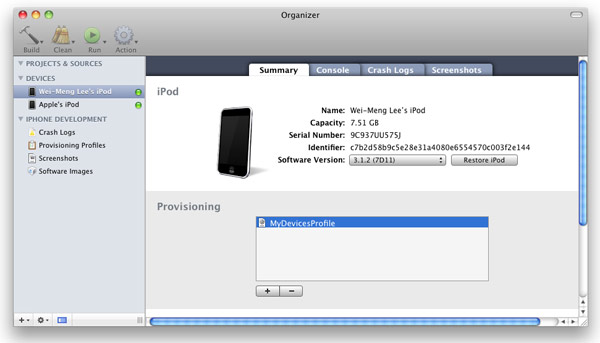 Figure 18
Figure 18. Viewing the installed provisioning profile
Creating the iPhone Application
1. In Xcode, create a new View-Based Application project and name it as ApplePushNotification.
2. Drag and drop a WAV file (shown as
beep.wav in this example) onto the Resources folder in Xcode (see Figure 19).
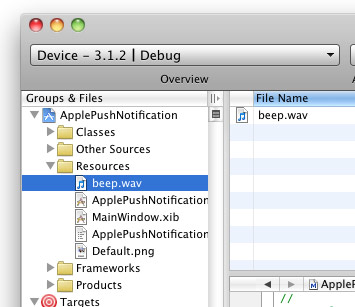 Figure 19
Figure 19. Adding a WAV file to the project
Expand on the Targets item in Xcode and select the ApplePushNotification item. Press Command-I. In the Info window, click the Properties tab (see Figure 20).
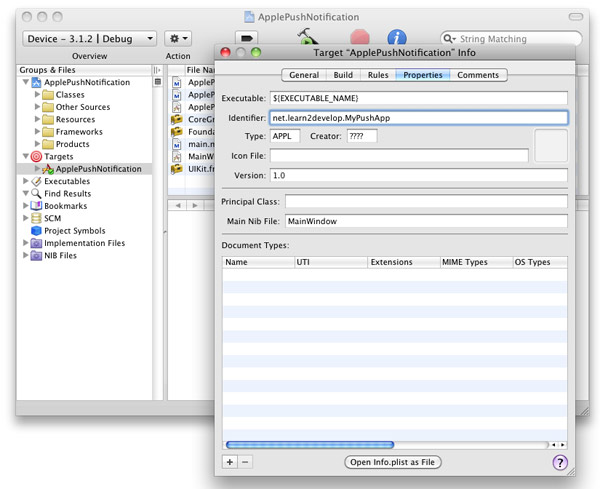 Figure 20
Figure 20. Entering the App ID for the application
In the Identifier textbox, type <
net.learn2develop.MyPushApp.
4. Click on the Build tab and type "Code Signing" in the search box. In the Any iPhone OS Device item, select the profile as shown in Figure 21:
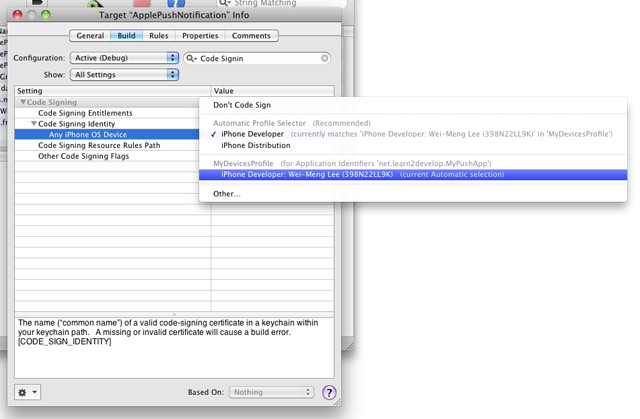 Figure 21
Figure 21. Selecting the profile for code signing
In the
ApplePushNotificationAppDelegate.m file, type the following code in bold:
#import "ApplePushNotificationAppDelegate.h"
#import "ApplePushNotificationViewController.h"
@implementation ApplePushNotificationAppDelegate
@synthesize window;
@synthesize viewController;
- (void)applicationDidFinishLaunching:(UIApplication *)application {
[window addSubview:viewController.view];
[window makeKeyAndVisible];
NSLog(@"Registering for push notifications...");
[[UIApplication sharedApplication]
registerForRemoteNotificationTypes:
(UIRemoteNotificationTypeAlert |
UIRemoteNotificationTypeBadge |
UIRemoteNotificationTypeSound)];
}
- (void)application:(UIApplication *)app didRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithDeviceToken:(NSData *)deviceToken {
NSString *str = [NSString
stringWithFormat:@"Device Token=%@",deviceToken];
NSLog(str);
}
- (void)application:(UIApplication *)app didFailToRegisterForRemoteNotificationsWithError:(NSError *)err {
NSString *str = [NSString stringWithFormat: @"Error: %@", err];
NSLog(str);
}
- (void)application:(UIApplication *)application didReceiveRemoteNotification:(NSDictionary *)userInfo {
for (id key in userInfo) {
NSLog(@"key: %@, value: %@", key, [userInfo objectForKey:key]);
}
}
- (void)dealloc {
[viewController release];
[window release];
[super dealloc];
}
@end 6. Press
Command-R to test the application on a real device. Press
Shift-Command-R in Xcode to display the Debugger Console window. Observe carefully the device token that is printed (see Figure 22). In the figure below, the token is:
38c866dd bb323b39 ffa73487 5e157ee5 a85e0b7c e90d56e9 fe145bcc 6c2c594b. Record down this device token (you might want to cut and paste it into a text file).
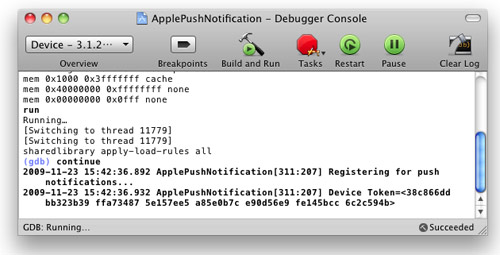 Figure 22
Figure 22. Viewing the device token for push notification
7. If you go to the Settings application on your iPhone/iPod Touch, you will notice that you now have the Notifications item (see Figure 23).
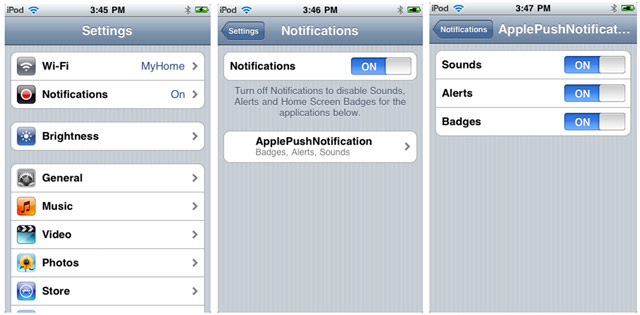 Figure 23
Figure 23. Viewing the Notifications item in the Settings application
Creating the Push Notification Provider
A Push Notification provider is an application written by the application's developer to send push notifications to the iPhone application through the APNs.
Here are the basic steps to send push notifications to your applications via the Apple Push Notification Service (APNs):
1. Communicate with the APNs using the SSL certificate you have created earlier.
2. Construct the payload for the message you want to send.
3. Send the push notification containing the payload to the APNs.
The APNs is a stream TCP socket that your provider can communicate using a SSL secured communication channel. You send the push notification (containing the payload) as a binary stream. Once connected to the APNs, you should maintain the connection and send as many push notifications as you want within the duration of the connection.
Tip: Refrain from opening and closing the connections to the APNs for each push notification that you want to send. Rapid opening and closing of connections to the APNs will be deemed as a Denial-of-Service (DOS) attack and may prevent your provider from sending push notifications to your applications.
The format of a push notification message looks like Figure 24 (figure from Apple's documentation):
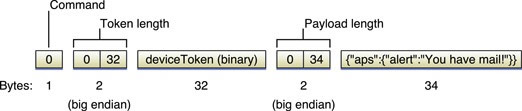 Figure 24
Figure 24. Format of a push notification message
For more details, please refer to
Apple Push Notification Service Programming Guide.
The payload is a JSON formatted string (maximum 256 bytes) carrying the information you want to send to your application. An example of a payload looks like this:
{
"aps": {
"alert" : "You got a new message!" ,
"badge" : 5,
"sound" : "beep.wav"},
"acme1" : "bar",
"acme2" : 42
} To save yourself the trouble in developing a push notification provider from scratch, you can use the
PushMeBaby application (for Mac OS X) written by Stefan Hafeneger (Get it
here).
1. Open the PushMeBaby application in Xcode.
2. Right-click on the Resources folder in Xcode and select Add Existing Files…. Select the
aps.developer.identity.cer file that you have downloaded earlier (see Figure 25).
 Figure 25
Figure 25. Adding the SSL certificate to the application
In the
ApplicationDelegate.m file, modify the code as shown in bold below:
- (id)init {
self = [super init];
if(self != nil) {
self.deviceToken = @"38c866dd bb323b39 ffa73487 5e157ee5 a85e0b7c e90d56e9 fe145bcc 6c2c594b";
self.payload = @"{\"aps\":{\"alert\":\"You got a new message!\",\"badge\":5,\"sound\":\"beep.wav\"},\"acme1\":\"bar\",\"acme2\":42}";
self.certificate = [[NSBundle mainBundle]
pathForResource:@"aps_developer_identity" ofType:@"cer"];
}
return self;
} 4. Press Command-R to test the application. You will be asked to grant access to the certificate. Click Always Allow (see Figure 26):
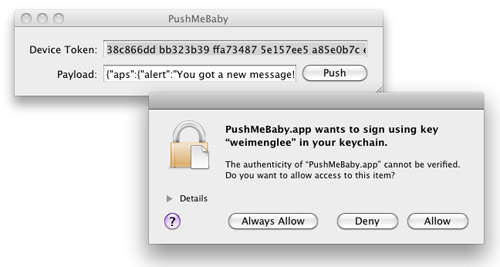 Figure 26
Figure 26. Granting access to the SSL certificate
On the iPhone/iPod Touch, ensure that the ApplePushNotification application is not running. To send a message to the device, click the Push button. The server essentially sends the following message to the Apple Push Notification server:
{
"aps": {
"alert" : "You got a new message!" ,
"badge" : 5,
"sound" : "beep.wav"},
"acme1" : "bar",
"acme2" : 42
} 5. If the message is pushed correctly, you should see the notification as shown in Figure 27.
 Figure 27
Figure 27. Receiving a Push Notification message
If you now debug the ApplePushNotification application by pressing
Command-R and send a push message from the PushMeBaby application, the Debugger Console window will display the following outputs:
2009-11-24 21:11:49.182 ApplePushNotification[1461:207] key: acme1, value: bar
2009-11-24 21:11:49.187 ApplePushNotification[1461:207] key: aps, value: {
alert = "You got a new message!";
badge = 5;
sound = "beep.wav";
}
2009-11-24 21:11:49.191 ApplePushNotification[1461:207] key: acme2, value: 42 Summary
In this article, you have seen the various steps required to build an iPhone application that utilizes Apple's Push Notification service.































